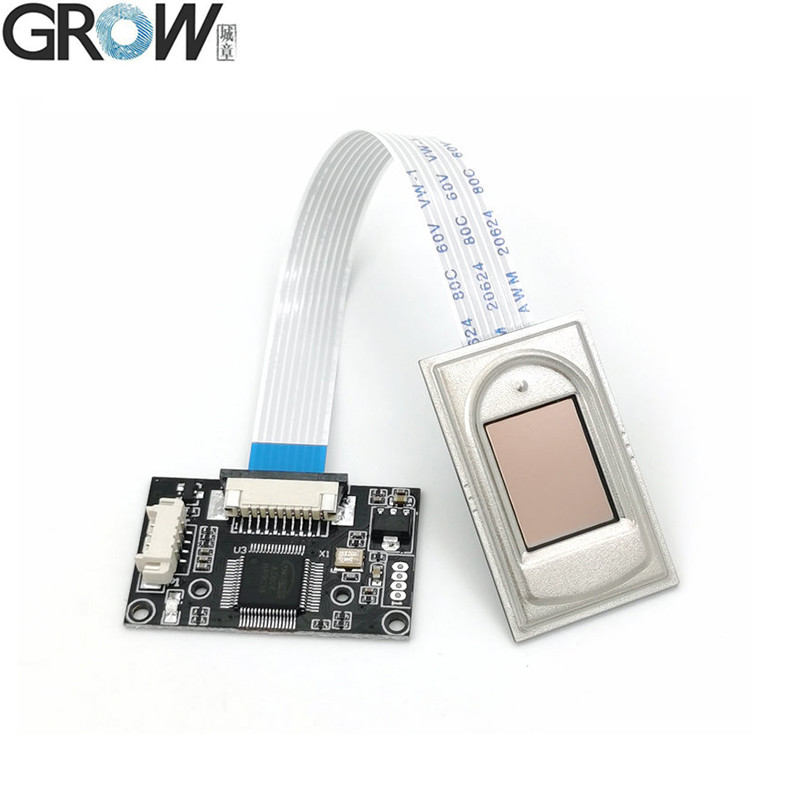
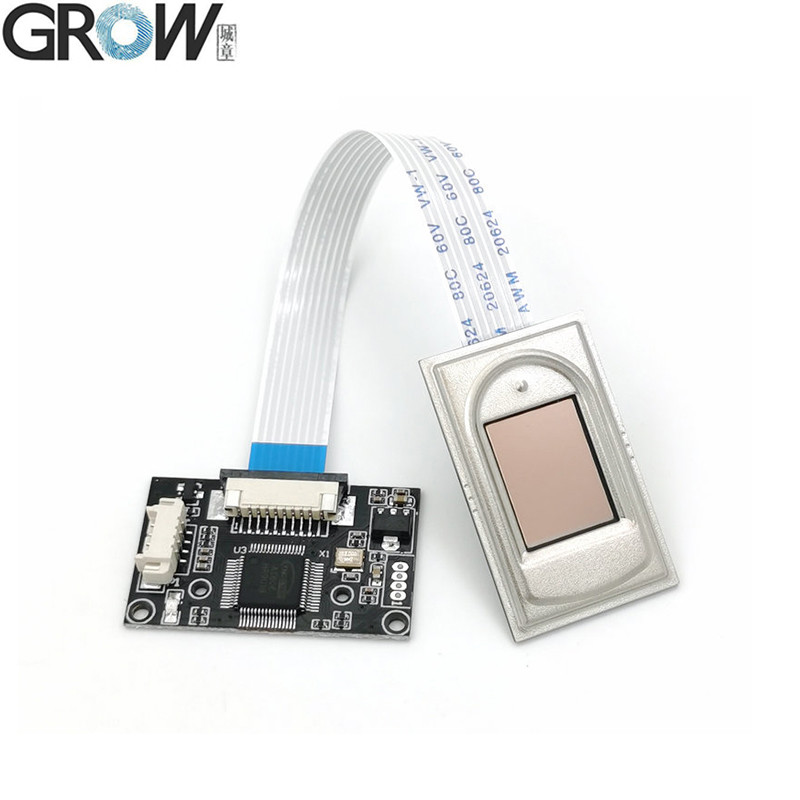
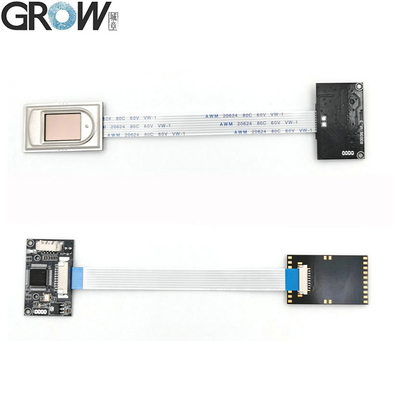
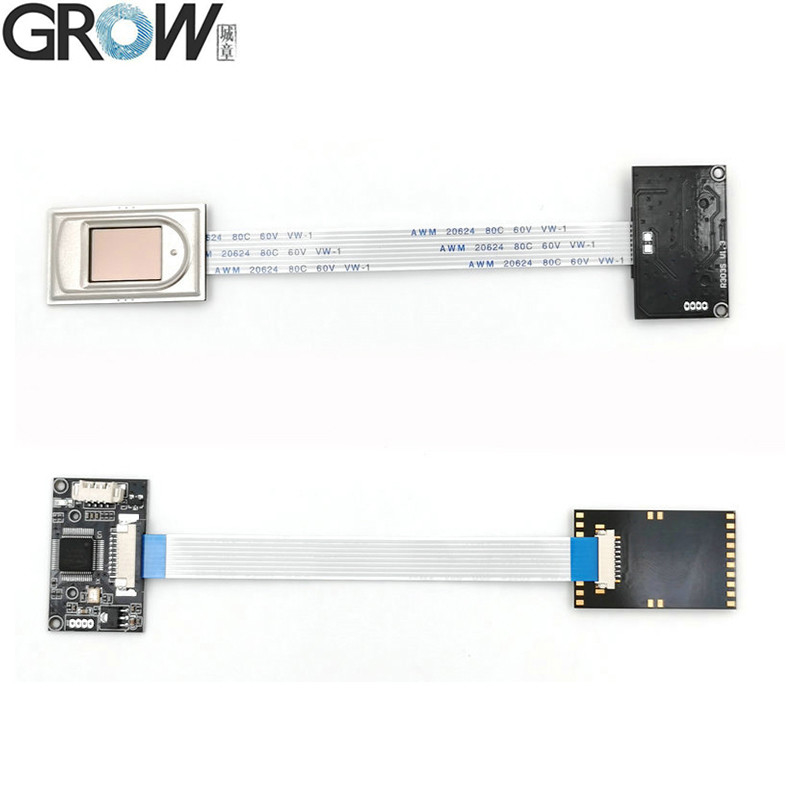
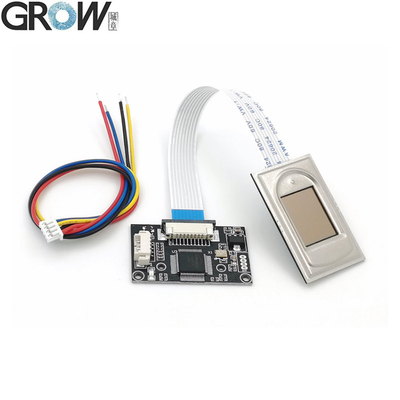
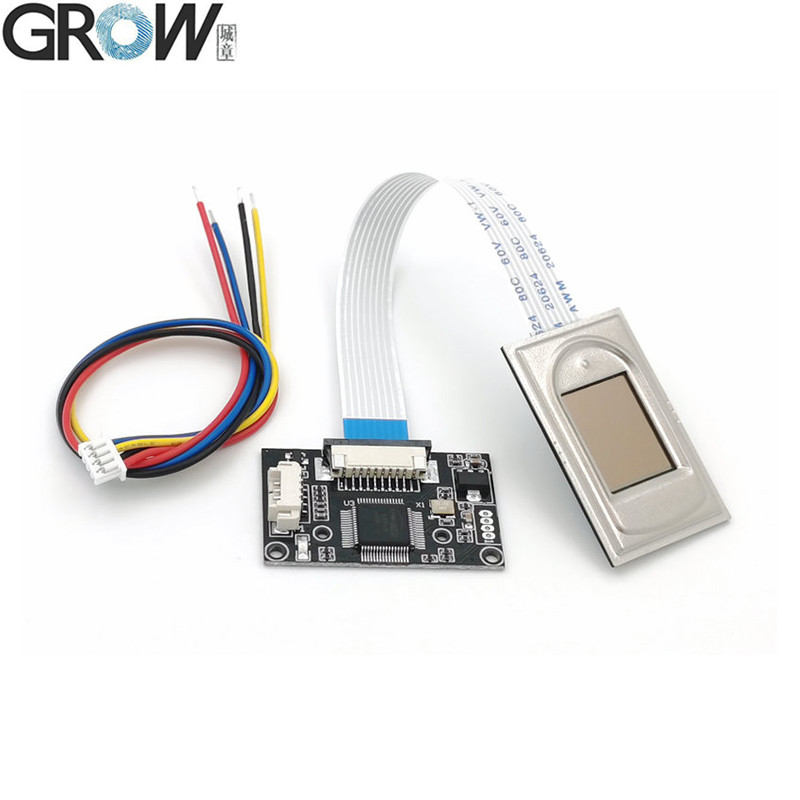
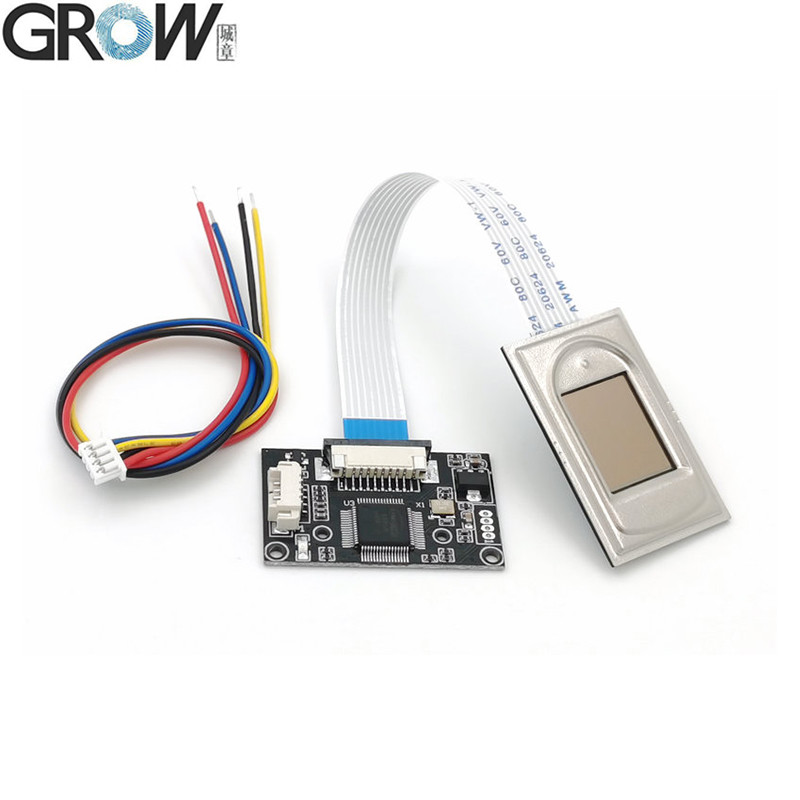
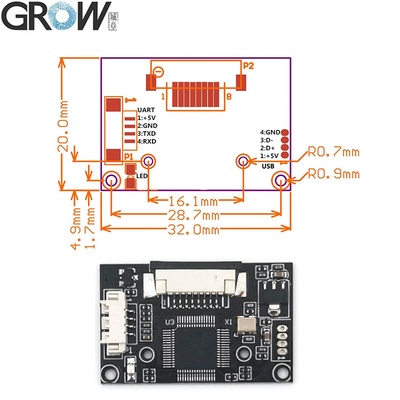
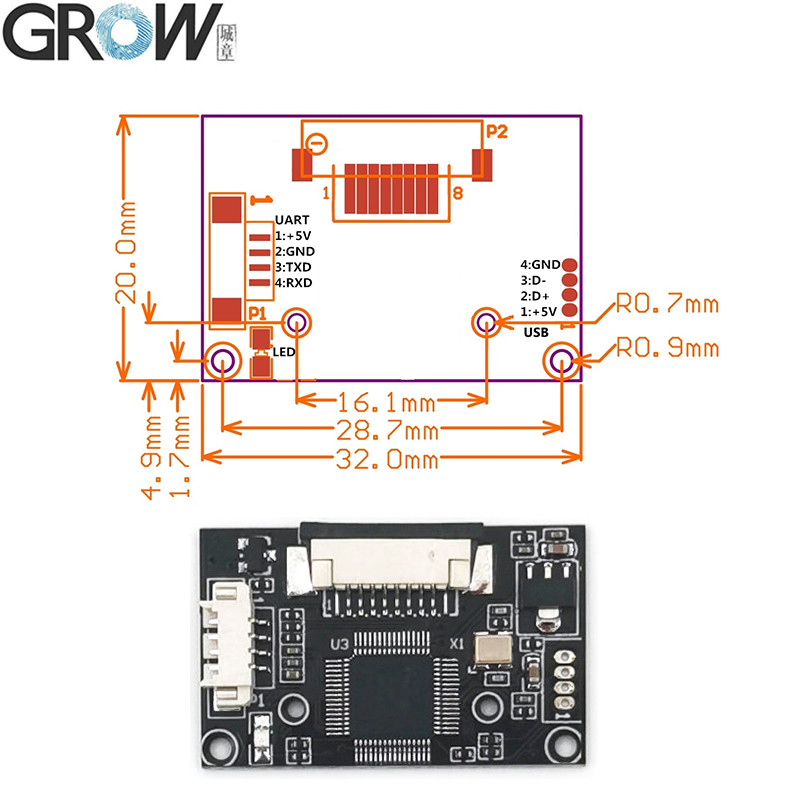
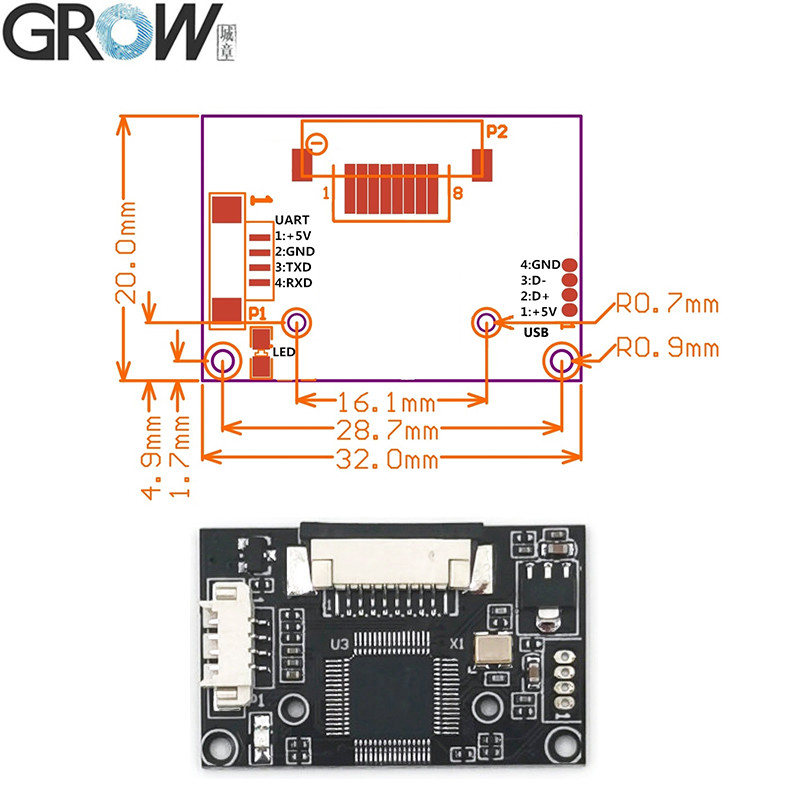
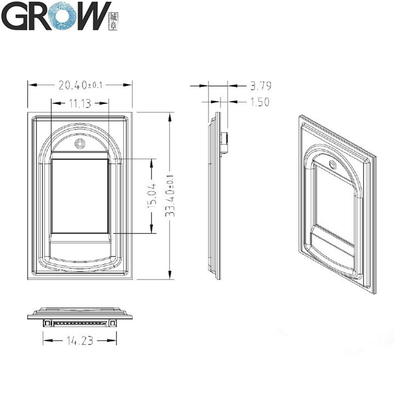
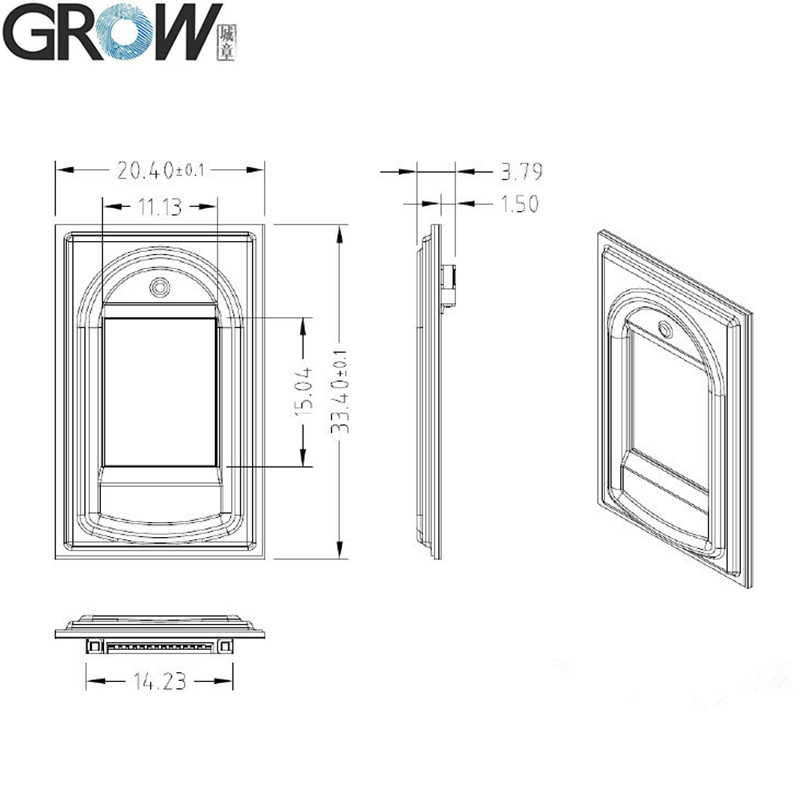
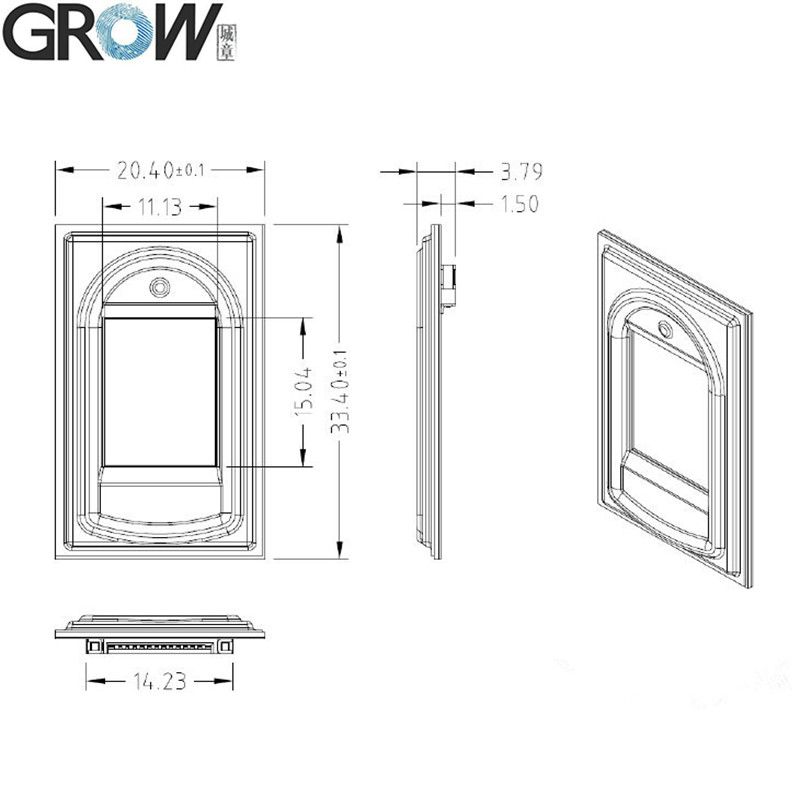
Description
·Communication interface : USB and UART
·1:N Identification (One-to-Many)
·1:1 Verification (One-to-One)
·High speed fingerprint identification algorithm engine
·Self study function
·Fingerprint feature data read/write functions
·Get Feature Data of Captured fingerprint and Verify/Identify Downloaded Feature with Captured
·Fingerprint Identify Downloaded Feature with Captured fingerprint
·Security Level setting
·Able to set BaudRate/ Device ID/Device Password
·Operating system:Windows 98, Me, NT4.0, 2000, XP,WIN 7 or Android
Specifications
·Interface:USB 2.0 and UART(3.3V-TTL logic)
·Resolution:508 DPI
·Work Current: <55mA
·Voltage: DC 4.2-6.0V
·Fingerprint capacity:1000
·Security Level: 1-5, default is 3
·Sensor Array: 208*288 pixel
·Fingerprint reader module size: 20.4 * 33.4 (mm)
·Effective collection area: 11 * 15 (mm)
·ScanningSpeed: < 0.2 second
·Verification Speed: < 0.3 second
·Matching Method: 1:1; 1:N
·FRR (False Rejection Ratio): ≤0.01%
·FAR (False Acceptance Ratio): ≤0.00001%
·Work environment: -20°C ---55°C
·Work Humidity: 20-80%
·Communications baud rate (UART): (9600 × N) bps where N = 1 ~ 12(default N = 6, ie 57600bps)
Files
·All fingerprint module support with Arduino, Android, Windows, Linux, .Net and so on.
·Provide Free SDK Files
·Provide User Manual
How secure is fingerprint recognition?
Fingerprint recognition has high security, but it is not foolproof. Its security mainly depends on the following aspects:
1. Difficult to replicate
Fingerprints have uniqueness and stability. Compared to traditional password and pattern unlocking, fingerprint recognition is more difficult to forge. On the one hand, fingerprint images need to be collected through specific sensors, and high-precision replication requires professional equipment. On the other hand, certain devices, such as ultrasonic fingerprint sensors, also have the ability to detect blood flow and live features, further enhancing safety.
2. Encrypt storage and transmission
In smart devices, fingerprint data is usually not directly stored as an image, but is converted into feature data through hash functions or other encryption algorithms and stored in a secure area of the device (such as Apple's Secure Enclave or Android's Trust Zone). During each verification, the device compares real-time fingerprint data with stored feature data. The entire process adopts end-to-end encryption to ensure that data is not easily intercepted by hackers.
3. Prevent forgery attacks
Although fingerprint recognition has high security, it is not unbreakable. For example, early capacitive fingerprint sensors could be deceived through silicone models or fingerprint imitation. To cope with this type of attack, current sensor technology is constantly improving, not only adding live detection capabilities, but also combining other biometric features (such as facial recognition, iris scanning) for dual verification, thereby further enhancing anti-counterfeiting capabilities.
4. Impact of environmental factors
One issue with fingerprint recognition is the impact of the environment on its recognition accuracy. For example, when the user's fingers are wet, dry, dirty, or have wounds, the fingerprint image may not be fully captured, resulting in recognition failure. In this case, some devices allow users to set multiple fingerprints to increase the success rate of unlocking.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!