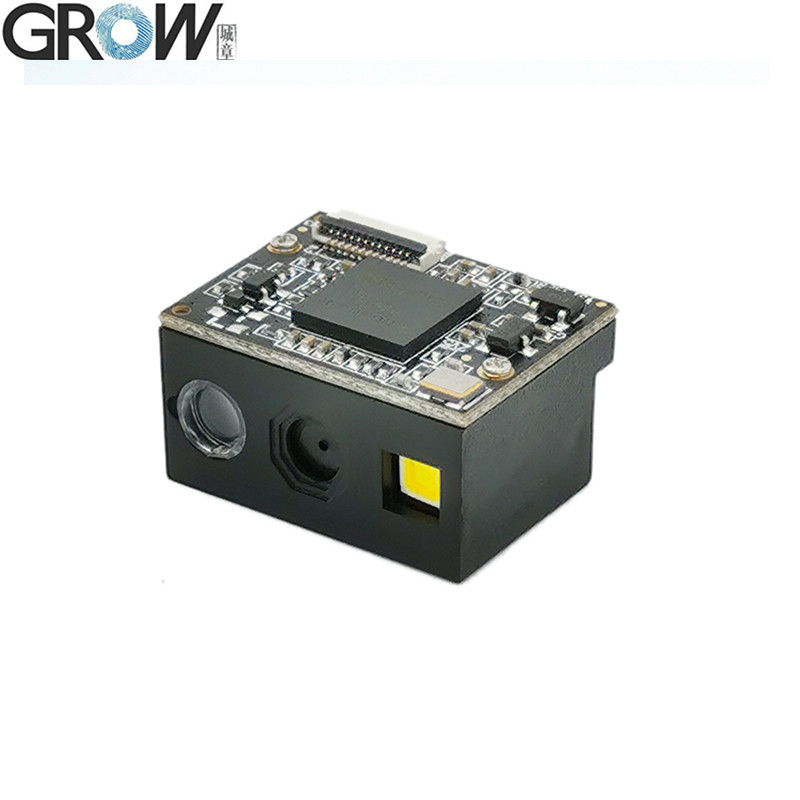
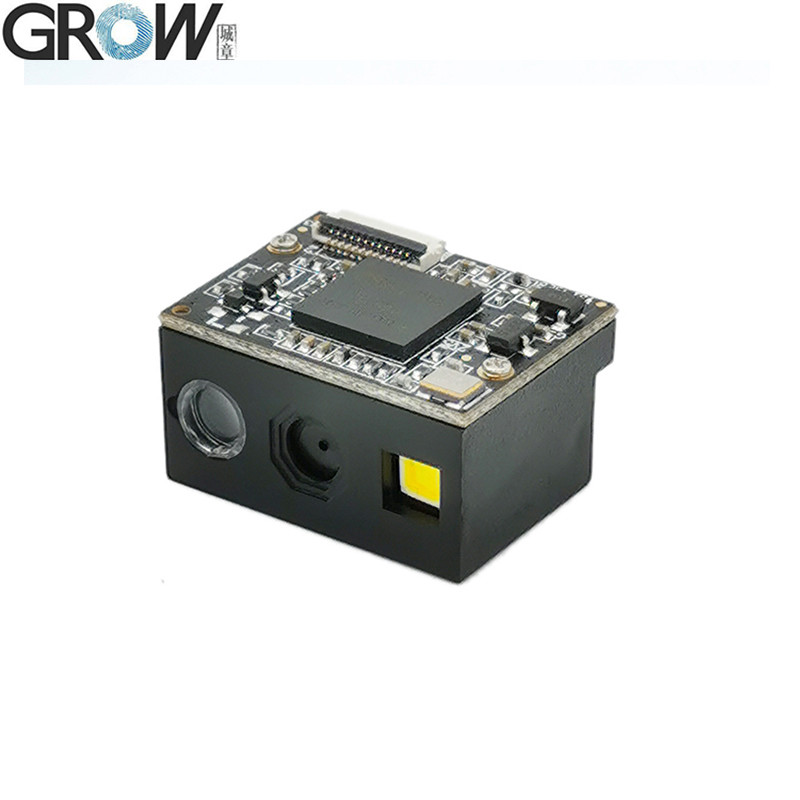
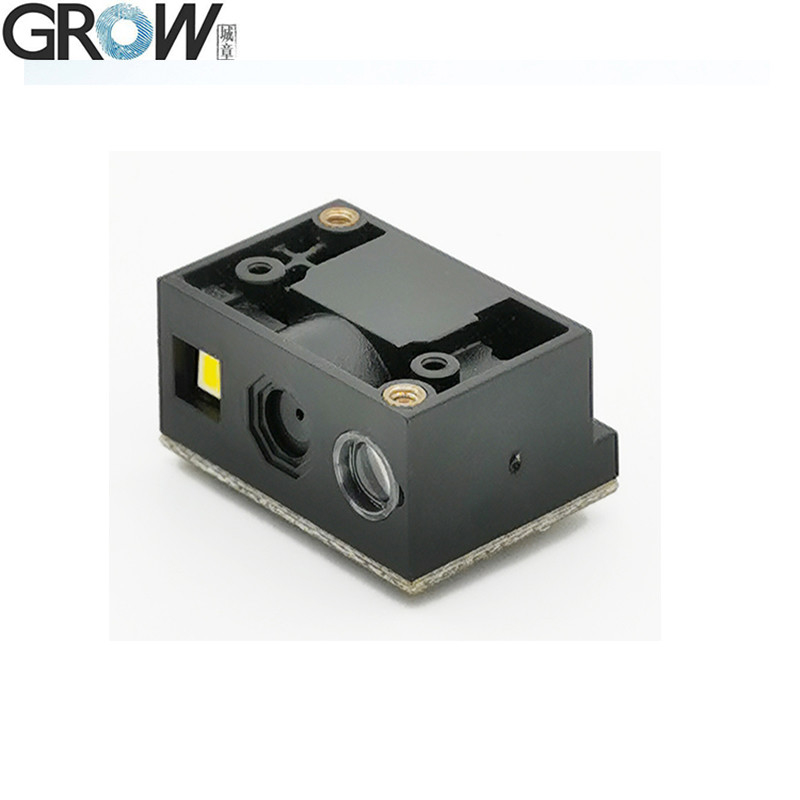
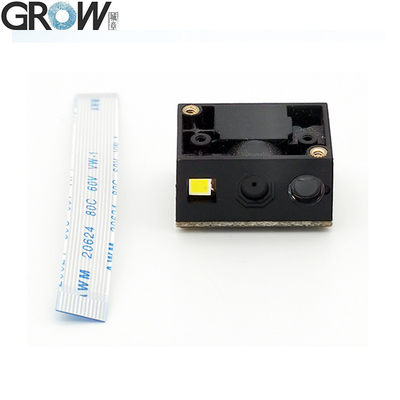
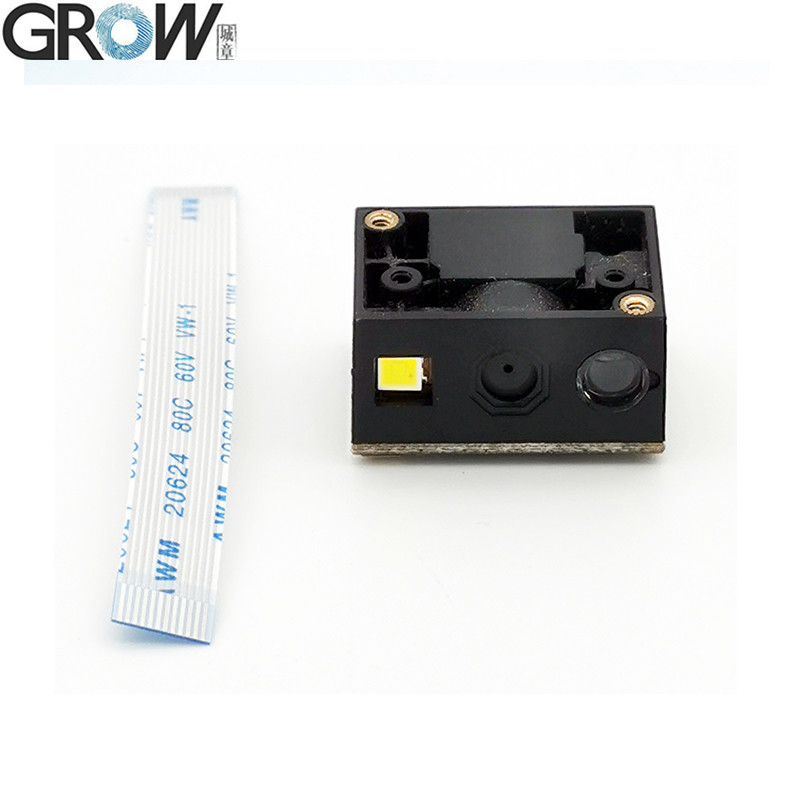
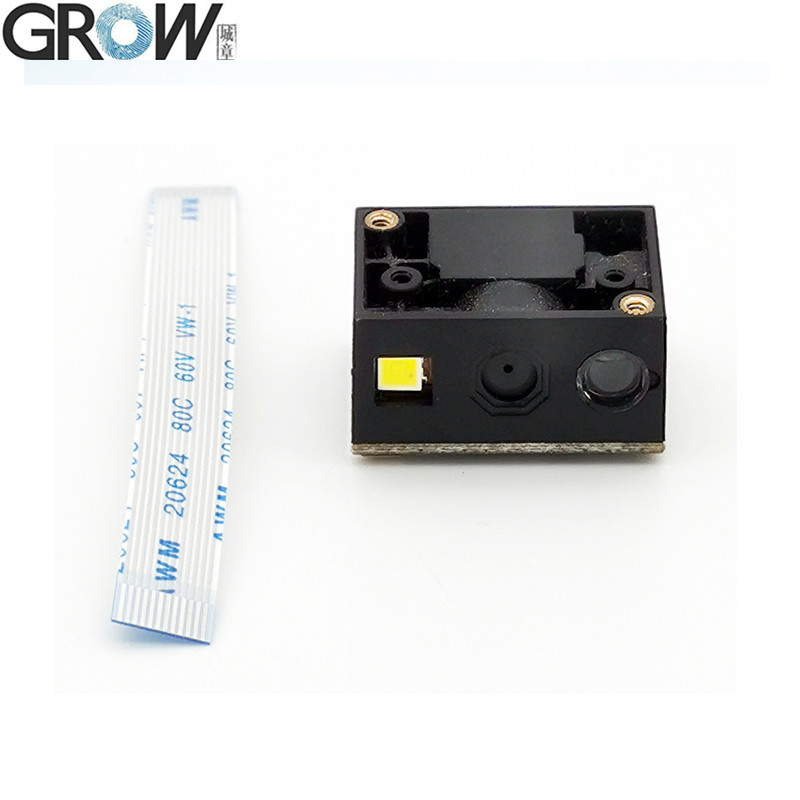
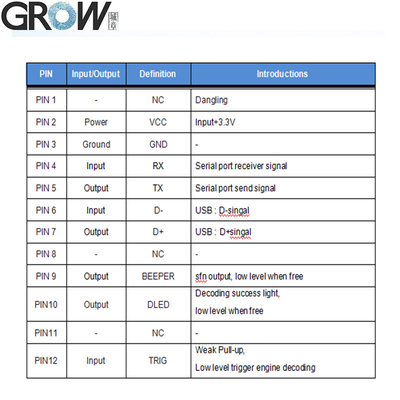
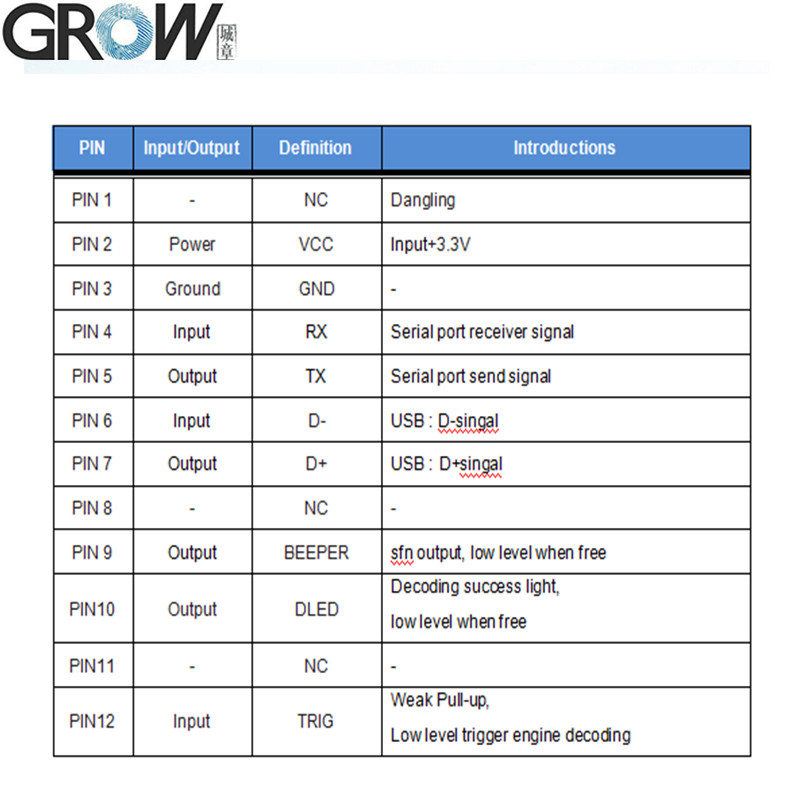
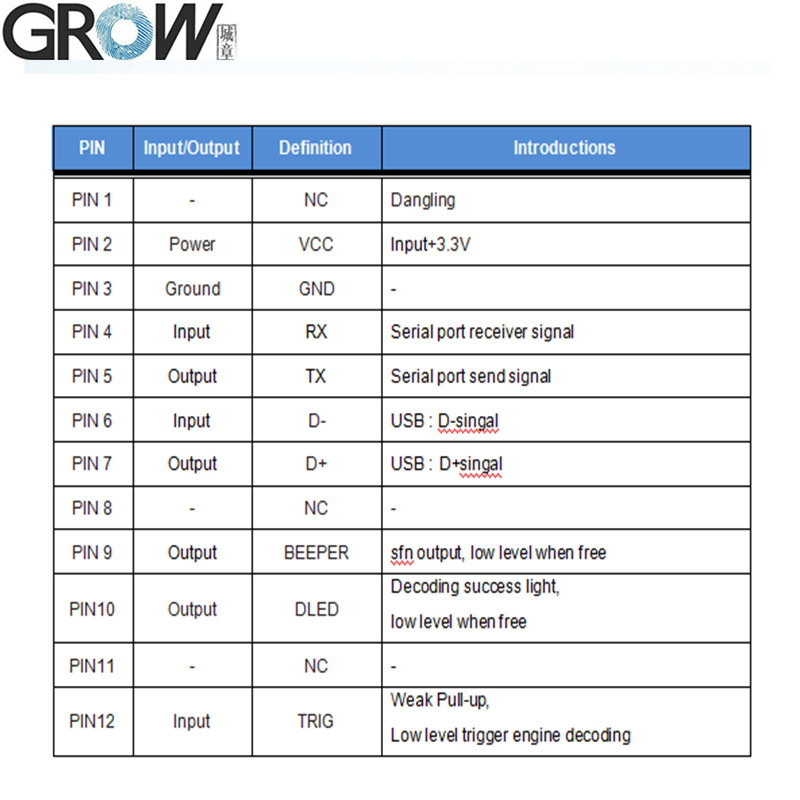
Description
1. USB wired barcode scanner to capture 1D, 2D code on labels, paper, mobile phone or computer.
2. High-efficiency recognization and high upload speed for improving your working efficiency.
3. With buzzer for reminding you that the scanning successfully or not.
4. Compatible with USB and UART interface.
5. Over 180 configurable options
6. Macro support replace a string in the bar code with another
7. Programmable preamble postamble and termination strings
8.Superior reading performance utilizing advanced decoding algorithms
Specifications
|
Scanning Performance
|
Scan Mode
|
1280*800 CMOS
|
|
Lighting
|
White LED
|
|
Collimate
|
Red LED
|
|
Read Code
Type
|
2D
|
QR Code, Data Matrix, PDF417,Aztec,Micro QR,
Micro PDF417,Maxicode,Hanxin Code
|
|
1D
|
EAN,UPC,Code 39,Code 93,Code 128,UCC/EAN 128, Codabar,
|
|
Interleaved 2 of 5, ITF-6,ITF-14,ISBN,ISSN, MSI-Plessey
|
|
GS1 Databar ,Code 11,Industrial 2 of 5,GS1 Composite
|
|
Standard 2 of 5,Plessey, Matrix 2 of 5
|
|
Accuracy of reading
|
1D≥4mil , 2D≥7.54mil
|
|
Depth of Field
|
EAN-13
|
35mm-220mm (13mil 13byte)
|
|
|
Code 39
|
30mm-135mm (5mil 4 byte)
|
|
QR Code
|
45mm-460mm (20mil 16 byte)
|
|
Data Marix
|
25mm-180mm (10mil 20 byte)
|
|
PDF417
|
30mm-160mm (6.67mil 7 byte)
|
|
Contrast
|
≥25%
|
|
Scanning angle
|
Intersection angle 360°,Elevation ± 55°
Deflection angle ± 55°
|
|
Viewing Angle
|
H:52° V:38°
|
|
Mechanical/
Electrical Parameters
|
Interface
|
TTL-232 , USB (HID-KBW, Virtual serial port)
|
|
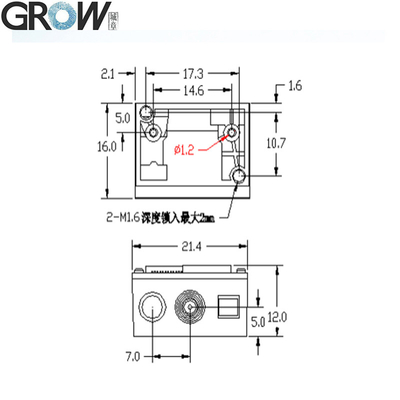
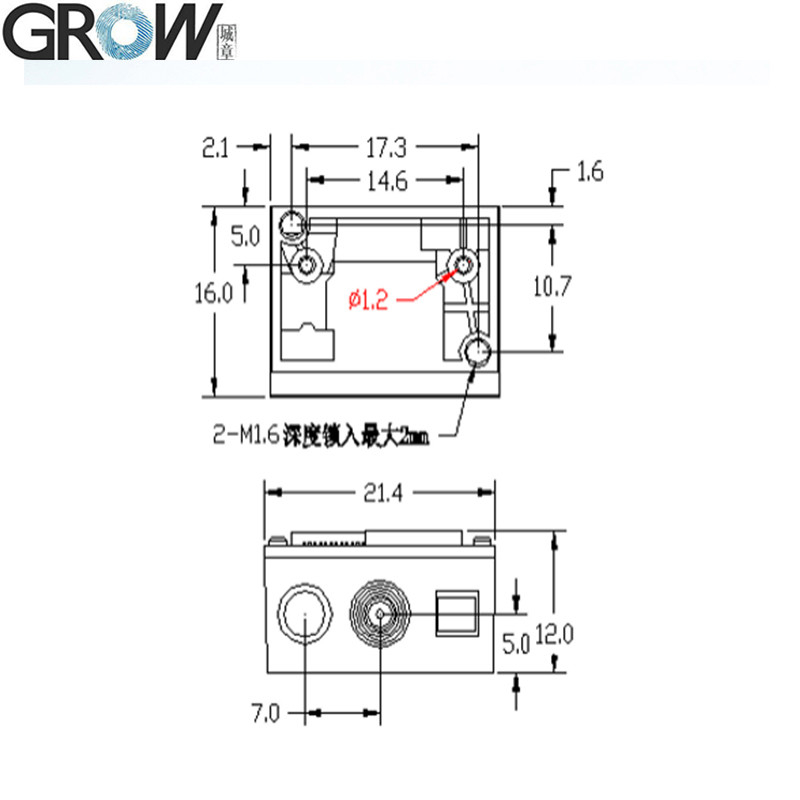
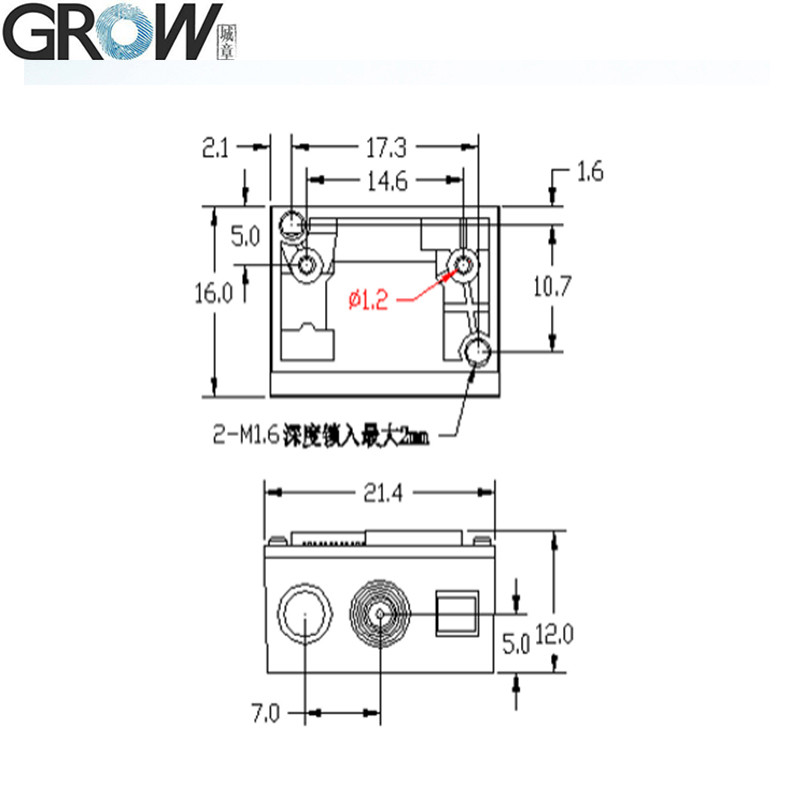
Dimension
|
21.4(W)*16(D)*12(H)mm
|
|
Operating Voltage
|
DC 3.3V
|
|
Operating Current
|
180mA
|
|
Environmental Parameters
|
Operating Temperature
|
-20℃~+50℃
|
|
Storage Temperature
|
-40℃~+70℃
|
|
Operating Humidity
|
5%~95%(Non-Condensing)
|
|
Environmental Light
|
0~100000LUX
|
Files
·Provide User Manual
You can download the GM69-S user manual from this website link:
https://hzgrow.en.made-in-china.com
Is the QR code scanning module suitable for embedding in self-service systems?
With the sweeping wave of digitalization, self-service systems have been widely deployed in various industries, such as ordering self-service machines in fast food chains (such as McDonald's and KFC), unmanned vending machines in supermarkets, and self-service registration and payment systems in hospitals. In these self-service platforms, the integration of QR code scanning technology is becoming increasingly significant. However, there is still room for discussion about whether it is perfectly adapted to self-service systems.
Self service system, as the core component of modern service industry, aims to optimize service processes, reduce labor costs, and provide users with more convenient and personalized service enjoyment through automation and intelligence. In this context, the rapid and accurate capture of information has become the cornerstone of the smooth operation of self-service systems. The integration of QR code scanning technology has significantly enhanced the operational efficiency and user service experience of self-service devices. Users only need to display the QR code on their mobile devices, and the system can instantly recognize and process it, eliminating the tedious manual typing or card verification steps and greatly simplifying the operation process. In addition, QR code scanning also has excellent security performance and flexibility, supporting customized development according to specific needs and flexibly responding to diverse application scenarios.
In the field of self-service devices, whether it is self-service ordering machines, vending machines, information query terminals, ticket machines, or medical self-service stations, integrating high-performance and cost-effective QR code scanning modules can significantly enhance the market competitiveness of enterprises. By integrating high-performance scanning devices or adapting professional one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and even long-distance scanning components, users can easily complete scanning actions, effectively saving time. The application scope of QR code scanning technology is wide, not limited to the above-mentioned devices, but also includes comprehensive cash register machines, library self-service borrowing and returning systems, and hospital self-service registration and payment machines.
However, the decision to embed QR code scanning technology still needs to consider factors such as the specific application scenarios, target user groups, and cost budget of the self-service system. For example, in situations where frequent interaction and information updates are required (such as self-service ticketing machines, vending machines, and access control gates), QR code scanning technology is undoubtedly the preferred choice; In scenarios with extremely high security requirements and special demands for device stability (such as ATM machines), it is necessary to weigh comprehensively and make prudent decisions.
In summary, QR code scanning technology is suitable for integration into self-service systems in most cases. It can effectively improve the interaction efficiency and user satisfaction of the system, but the specific adoption still needs to be carefully considered based on actual needs. With the continuous evolution of technology and the deepening of applications, we are confident that QR code scanning technology will demonstrate its important value in more fields, leading self-service systems to develop towards a more intelligent and convenient direction.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!